Difference between revisions of "6502"
From SizeCoding
Childishbeat (talk | contribs) m (Childishbeat moved page 6502 based CPUs to 6502: Less verbose) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
* Synthetic instructions https://wiki.nesdev.com/w/index.php/Synthetic_instructions#8-bit_rotate | * Synthetic instructions https://wiki.nesdev.com/w/index.php/Synthetic_instructions#8-bit_rotate | ||
| − | == | + | == 6502 Based Platforms == |
| − | + | *'''[[Atari 8Bit]]''' - Atari 8-Bit Family (Atari XL/XE, etc.) | |
| − | + | *'''[[Apple II]]''' - Apple II(e) | |
| − | + | *'''[[Commodore 64]]''' - Commodore 64 | |
| − | + | *'''[[BBC Micro]]''' - Acorn BBC Micro/Master/Electron. | |
| − | + | *'''[[Atari Lynx]]''' - Atari Lynx Handheld | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * Atari | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 10:41, 8 April 2022
Contents
Introduction
Wanting to start sizecoding on a 6502 platform in this day and age can be tough.
So here is a bit of help to get you started:
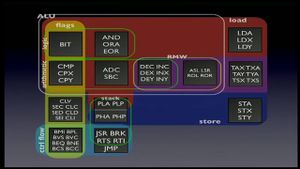
The 6502 processor
The 6502 processor can be seen as the 8-bit micro ARM chip. It has only has 3 registers (Accumulator, X and Y registers) and a handful of instructions to work with.
Adressing modes
To be added.
Zero page
When using the 6502 for sizecoding, you'll mostly be working from zeropage
General 6502 Resources
- 6502.org http://www.6502.org/
- 6502 instruction reference http://www.6502.org/tutorials/6502opcodes.html
- 6502 books http://retro.hansotten.nl/6502-sbc/
- 6502 Assembler tutorial https://dwheeler.com/6502/oneelkruns/asm1step.html
- Easy 6502 code tester https://skilldrick.github.io/easy6502/
- Synthetic instructions https://wiki.nesdev.com/w/index.php/Synthetic_instructions#8-bit_rotate
6502 Based Platforms
- Atari 8Bit - Atari 8-Bit Family (Atari XL/XE, etc.)
- Apple II - Apple II(e)
- Commodore 64 - Commodore 64
- BBC Micro - Acorn BBC Micro/Master/Electron.
- Atari Lynx - Atari Lynx Handheld